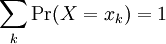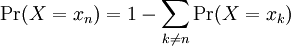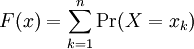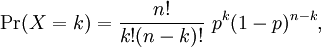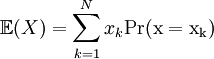Random variable
- A discrete random variable X is a quantity that can assume any value x from a discrete list of values with a certain probability.
- The probability that the random variable X assumes the particular value x is denoted by Pr(X = x). This collection of probabilities, along with all possible values x, is the probability distribution of the random variable X.
| Discrete Probability Rules |
|---|
|
| Cumulative Distribution Function of a Discrete Random Variable |
|---|
| The cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a random variable X is denoted by F(x), and is defined as F(x) = Pr(X ≤ x). Using our identity for the probability of disjoint events, if X is a discrete random variable, we can write
where xn is the largest possible value of X that is less than or equal to x |
| Binomial PDF |
|---|
| If X is a binomial random variable associated to n independent trials, each with a success probability p, then the probability density function of X is:
where k is any integer from 0 to n. Recall that the factorial notation n! denotes the product of the first n positive integers: n! = 1·2·3···(n-1)·n, and that we observe the convention 0! = 1. |
| Definition: Expected Value of a Discrete Random Variable |
|---|
The expected value, 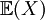 , of a random variable X is weighted average of the possible values of X, weight by their corresponding probabilities: , of a random variable X is weighted average of the possible values of X, weight by their corresponding probabilities:
where N is the number of possible values of X. |